Peripheral Blood Karyotyping
Chromosome analysis (karyotyping) is the microscopic evaluation of metaphase chromosomes for numerical and structural abnormalities associated with disease. An expert cytogenetic technologist analyzes the banded chromosomes at a microscope. Digital images of respective cells are captured and the chromosomes are arranged in a standard format known as a karyogram. Peripheral blood is the most common specimen type referred for analysis.
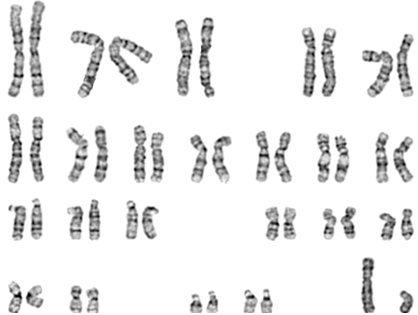
Normal Male Karyotype (46,XY)

Normal Female Karyotype (46,XX)
Bone Marrow & Leukemic Blood Chromosome Analysis
Bone marrow and leukemic blood samples that contain spontaneously dividing cells usually are cultured short-term without mitogens. Some specimens with B-cell conditions are stimulated with mitogens. Chromosome analysis of the dividing cells is useful in the diagnosis and classification of hematological malignancies
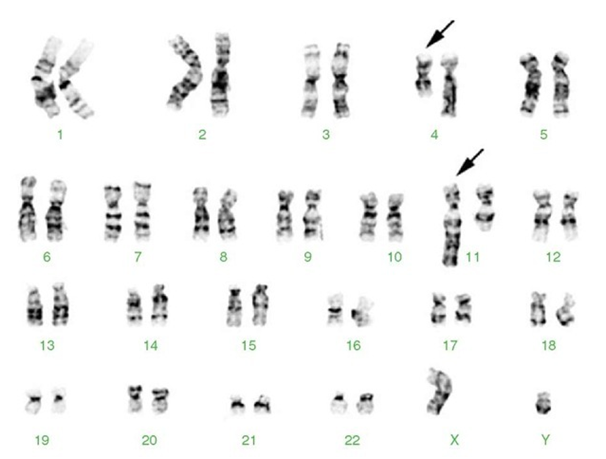
Abnormal karyotype image of a 10-year-old male with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): 46,XY,t(4;11)(q21;q23). Translocation of chromosome (4;11), was observed and is seen in 5-10%.
Fish
What is a FISH Test?
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a procedure that essentially creates a map of the genetic material in human cells, allowing cytogeneticists to locate specific DNA sequences on a chromosome. FISH technique gives useful insight in the understanding of certain genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities.
How Does FISH Testing Work?
Using molecular biology techniques, FISH testing detects the presence (or absence of) specific regions of the genome. Additionally, the Fluorescence in situ Hybridization procedure can be used to enumerate certain regions of the genome, depending on the circumstances.
Detection is accomplished by introducing fluorescently labeled pieces of DNA that are referred to as “probes”. Probes can be designed for any gene, size, or sequence. The process allows the cellular reproduction cycle to be mapped and analyzed.
When Is FISH Testing Used?
Cytogeneticists use FISH to identify genetic abnormalities related to cancer, as well as other diseases and conditions. In addition to being used for the purpose of detection, FISH can provide supplementary information that can be used to predict a patient’s response to certain treatment types.
Unlike most other techniques used to study chromosomes, FISH does not require actively dividing cells. This adds flexibility and increases the ability to identify and characterize cytogenetic abnormalities. Contact CMG to learn more about how we use FISH.
Fish - Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
Products of Conception (POC)
Indications for cytogenetic analysis on products of conception (POC) include recurrent spontaneous abortions, abnormalities on ultrasound prior to pregnancy loss, intrauterine growth retardation, confirmation of abnormal prenatal results, or pregnancy loss after IVF.
FLT3 – ITD ( Internal Tandem Duplication) mutation
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) mutations occur in almost 30% of all the AML cases, among which 25% of the mutations are internal tandem duplications (ITD).Several large-scale studies have confirmed that FLT3/ITD is strongly associated with leukocytosis and a poor prognosis in AML. Conversely, in a study from Shanghai, in the ALL patients, no FLT3/ITD mutations were detected. The earlier diagnosis of the FLT3 mutations help in the better understanding of the disease and also in the enabling of the targeted therapy that can help in achieving more durable remissions. Standardization and well-established clinical correlations make FLT3 mutational assessment by molecular methods a significant tool to decide among the treatment options and to determine AML prognosis.

Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling is a process through which knowledge about the genetic aspects of illnesses is shared by trained professionals with those who are at an increased risk or either having a heritable disorder or of passing it on to their unborn offspring. A genetic counsellor provides information on the inheritance of illnesses and their recurrence risks; addresses the concerns of patients, their families, and their health care providers supports patients and their families dealing with these illnesses.
Here at CMG, Prof P Thangaraju,PhD, Who has more than 40 years of experience in Genetics, counseled many patients with different Genetic disorders. Dr V G Dev, Founder and Adviser, CMG, would join through skype if necessary.
